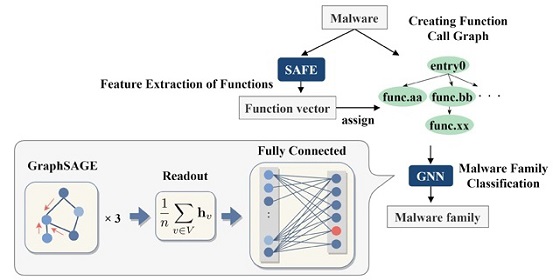
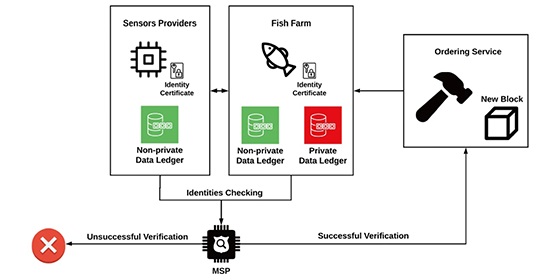
Journal of Surveillance, Security and Safety
Views: Downloads:
Views: Downloads:
Views: Downloads:
Views: Downloads:
Views: Downloads:
Views: Downloads:
Views: Downloads:
Views: Downloads:
Data
144
Authors
232
Reviewers
2020
Published Since
66,959
Article Views
24,040
Article Downloads
For Reviewers
For Readers
Add your e-mail address to receive forthcoming Issues of this journal:
Themed Collections
Data
144
Authors
232
Reviewers
2020
Published Since
66,959
Article Views
24,040
Article Downloads